Galerie
Slide shows
| Differenziertes Krafttraining | |
| Blum: Kinesiologische Analyse | |
| Unterkiefer | |
| Ren mobilis (Die Wanderniere) |
Schriftliches
| Title | Intertrochanteric Varus Osteotomy |
| Technique | Pencil / Watercolour |
| Author | Prof. Dr. Wagner, Orthopädische Klinik Schwarzenbruck/Nürnberg |
| Publication | Atlas of Hip Surgery |
| Publisher | Thieme Medical Publishers Inc., New York 1996 |
| close window | |
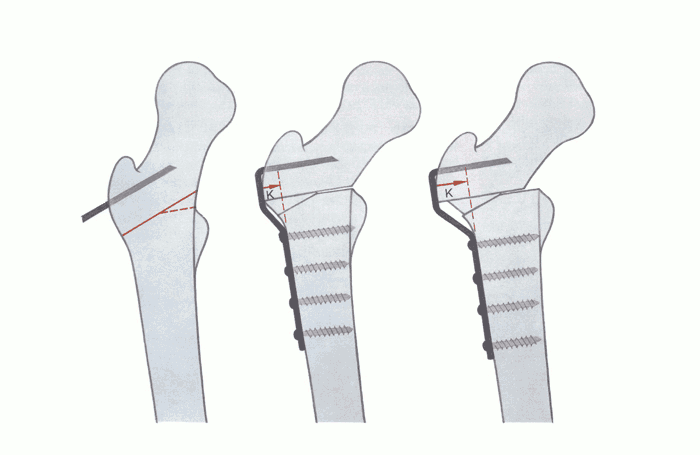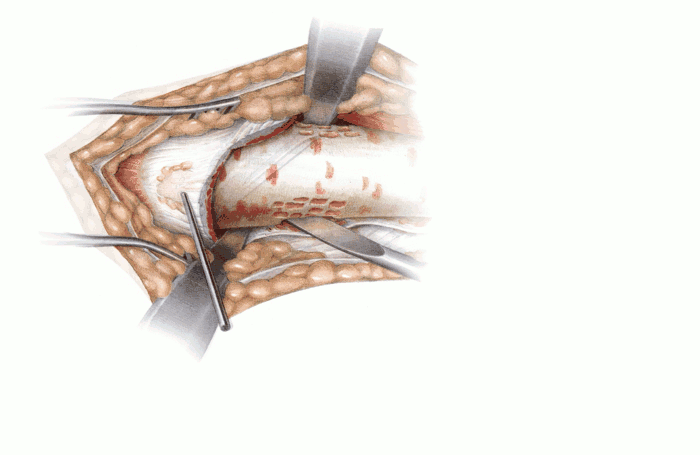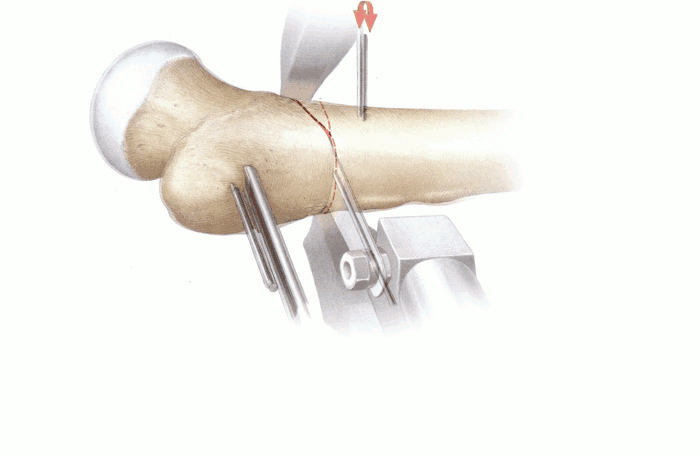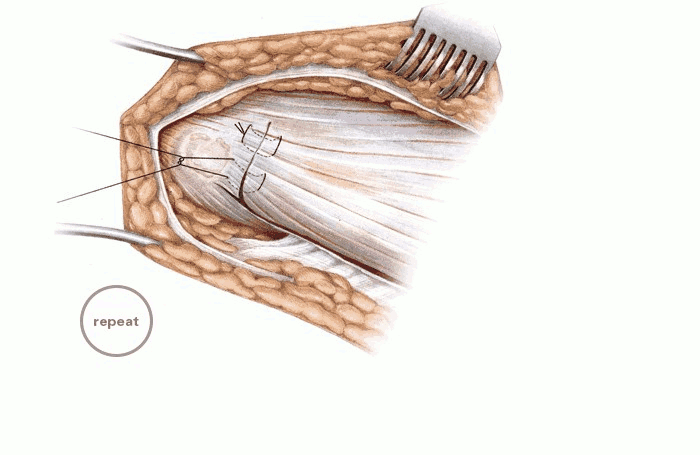
| Figure 1a-c | Shifting the distal fragment medially avoids the varus shift in the axis of the leg produced by the intertrochanteric varus osteotomy. |
| Figure 2/3 | The patient is positioned supine for a longitudinal skin incision over the lateral hip. |
| Figure 4 | After the fascia late is split, the origin of the vastus lateralis is dissected with an L-shaped incision distal to the most proximal aspect of the greater trochanter. |
| Figure 5 | The vastus lateralis is dissected from the femur and the lateral intermuscular septum and retracted anteriorly. |
| Figure 6 | The vastus lateralis is lifted with elevators. A marker wire is inserted into the greater trochanter to indicate the desired angle of correction. |
| Figure 7 | Decorticating the femoral cortex at the osteotomy site. |
| Figure 8 | The tendinous origin of the vastus lateralis is dissected from the surface of the bone distal to the marker wire to expose the osteotomy site for the blade of the angled blade plate. |
| Fig. 9-18 | Operation technique according to the diagram Figure 1 |
| Figure 19 | The vastus lateralis is reattached where it was transected with vertical mattress sutures. |
| close window | |